Intraoral radiography is one of the most essential tools in diagnosing dental and oral problems, providing exceptional capabilities for specialists when combined with extraoral radiography. In this article, we will explore these two imaging methods in detail, highlighting their differences, applications, and benefits. Additionally, we will answer frequently asked questions that are crucial for selecting the best imaging method.
Are you curious about which imaging method is better for you? Or perhaps you want to know the applications of panoramic imaging? All of this and more will be addressed below. Stay with us to gain comprehensive insights and better understand your needs.
Questions you’ll find answers to in this article:
- What issues can intraoral radiography detect?
- What are the benefits of extraoral radiography?
- What is the main difference between intraoral radiography and extraoral radiography?
- Is panoramic imaging part of intraoral or extraoral radiography?
- When should extraoral radiography be used?
To find answers to these questions and gain more detailed information, read the entire article!
Intraoral and extraoral radiography, as the two main dental imaging techniques, each have distinct applications and advantages. Recent studies have attempted to compare the capabilities and limitations of these two methods. Research indicates that intraoral scanners are highly accurate and efficient for three-dimensional imaging of structures like gum tissue and the alveolar process, excelling in smaller-scale imaging such as individual teeth (link). Additionally, innovative systems combining optical imaging and autofluorescence have enhanced the ability to evaluate oral tissues in depth (link).
On the other hand, extraoral radiography has demonstrated higher accuracy in full-arch scans compared to intraoral conditions but may be less precise in smaller-scale evaluations (link). Clinical conditions, such as changes in the oral environment, can impact the accuracy of intraoral scanners. However, error correction methods can improve their precision. Overall, intraoral scanners are better suited for smaller, more detailed applications, while extraoral scans are ideal for comprehensive imaging of arches and overall structures.
These findings suggest that the choice between the two methods should be based on specific clinical needs. For applications requiring high accuracy and small-scale details, intraoral radiography is preferred. In contrast, for broader evaluations, extraoral scanning is more suitable.
Intraoral or Extraoral Radiography: Which Is Better?
Intraoral radiography and extraoral radiography are two key methods in maxillofacial radiology, each with specific uses. In intraoral radiography, the sensor or film is placed inside the patient’s mouth, producing highly detailed images of the teeth and surrounding tissues. This method is particularly effective for identifying minor cavities, root issues, and evaluating precise dental restorations.
Conversely, in extraoral radiography, the imaging device is positioned outside the patient’s mouth, capturing broader images of the jaw, face, and surrounding structures. This technique is used to diagnose larger problems, such as jaw deformities, tumors, or sinus diseases.
The choice between these two methods depends on the patient’s needs. If high precision and small details are required, intraoral radiography is the better option. However, for examining larger issues or structures outside the teeth, extraoral radiography is recommended. Both methods have specific advantages and limitations, and the decision should be made in consultation with a specialist.
Applications of Intraoral Radiography in Dental Problem Diagnosis
Intraoral radiography is one of the most common and widely used methods in dentistry. Due to its high precision and detailed imaging, it is employed for diagnosing various dental and gum issues. One of its primary applications is detecting interproximal cavities that are not visible through routine examination. It is also used to evaluate the condition of tooth roots, identify dental infections, and assess restorations.
In intraoral radiography, localized images are captured, enabling dentists to focus on the target area with greater accuracy. As a result, this method is highly effective for complex treatments such as root canal therapy or dental implant placement. Furthermore, this type of imaging plays a significant role in diagnosing gum issues and preventing more advanced diseases.
Extraoral Radiography: Benefits and Drawbacks in Diagnosing Diseases
Extraoral radiography is essential for its ability to provide broader images of the jaw and facial structures. This method is particularly useful for patients with extensive issues, such as jaw deformities, bone fractures, or pre-surgical evaluations. Its primary advantage is offering a comprehensive view of dental and non-dental structures, enabling better diagnosis and planning for complex treatments.
However, this method has some drawbacks, including lower detail accuracy for individual teeth compared to intraoral radiography. Additionally, extraoral imaging typically involves higher costs and longer processing times. Nonetheless, its ability to visualize the entire jaw and facial region ensures its continued importance in maxillofacial radiology.
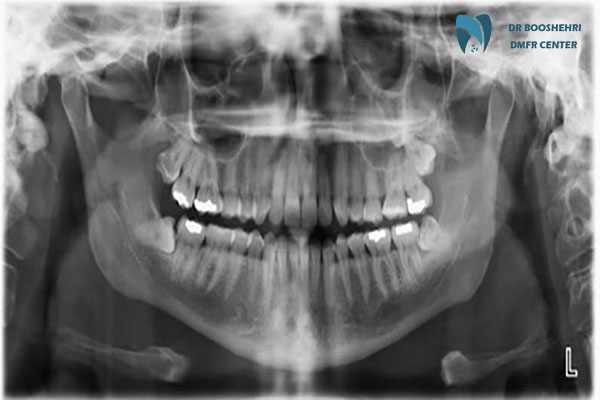
Compare intraoral radiography and extraoral radiography: Which one is better? Learn about the advantages and disadvantages of each and choose the right method for you.
Comparison of Intraoral and Extraoral Radiography for Precise Diagnosis
Comparing intraoral radiography and extraoral radiography requires a focus on diagnostic needs. Intraoral radiography is ideal for detecting minor issues like cavities or localized damage. Meanwhile, extraoral radiography is better suited for diagnosing broader problems or sinus-related diseases.
In many cases, a combination of both methods can enhance diagnostic accuracy. For instance, in patients requiring jaw surgery, intraoral imaging helps examine tooth details, while extraoral imaging aids in surgical planning. Therefore, the choice of the best method depends on the type of condition and treatment goals.
Role of Extraoral Imaging in Maxillofacial Radiology
In maxillofacial radiology, extraoral radiography is one of the main tools for examining complex problems. This method helps dentists and maxillofacial surgeons obtain a comprehensive view of the jaws, sinuses, and jaw joints. Panoramic, cephalometric, and CBCT imaging are examples of extraoral imaging techniques, each with specific applications.
One of the advantages of this method is the ability to detect hidden diseases or structural issues that cannot be seen with intraoral radiography. For instance, tumors, cysts, or complex fractures are better diagnosed with extraoral imaging. For this reason, this method holds a special place in diagnosing and treating maxillofacial problems.
Choosing Between Intraoral and Extraoral Imaging: Key Considerations
When choosing between intraoral radiography and extraoral radiography, several factors need to be considered. The type of issue, the level of precision required, and the purpose of the imaging are some of the most important factors. For minor dental issues, intraoral radiography is suitable due to its high precision and lower cost. However, for more extensive diseases or surgical planning, extraoral imaging would be a better choice.
Ultimately, consulting with a maxillofacial radiology specialist can help patients make the best decision. A correct imaging method not only aids in accurate diagnosis but also optimizes the treatment path.
Frequently Asked Questions by Patients at the Radiology Center Regarding Intraoral Imaging
What problems is intraoral radiography used for?
Intraoral radiography is used for diagnosing minor cavities, checking the condition of tooth roots, detecting dental infections, and assessing dental restorations. Due to its high precision, this method is suitable for local and minor problems and provides very detailed images of the teeth and surrounding tissues.
What are the benefits of extraoral radiography?
Extraoral radiography can provide a broad view of the jaws, face, sinuses, and jaw joints. This method is highly suitable for diagnosing structural abnormalities, sinus diseases, tumors, and jaw fractures. Additionally, the panoramic and CBCT images used in this technique assist in diagnosing and planning complex treatments such as jaw surgery.
What is the main difference between intraoral and extraoral radiography?
The main difference between these two methods lies in the placement of the imaging device and the type of issues they diagnose. In intraoral radiography, the sensor or film is placed inside the patient’s mouth, capturing detailed images of the teeth and surrounding tissues. In contrast, in extraoral radiography, the device is positioned outside the mouth to produce broader images of the jaw and facial structures.
Which category does panoramic imaging fall under?
Panoramic imaging is a type of extraoral radiography. This method provides a view of the entire upper and lower jaws, teeth, jaw joints, and sinuses in a single image. Panoramic imaging is especially useful for examining structural abnormalities, impacted teeth, and tumors.
When should extraoral radiography be used?
Extraoral radiography is recommended when broader issues need to be examined, such as jaw abnormalities, fractures, tumors, or sinus problems. This method is also suitable when planning jaw surgery or dental implants.
Choosing the Best Imaging Method with Dr. Boushehri’s Consultation
Both intraoral radiography and extraoral radiography play important roles in diagnosing and treating oral and jaw problems. This article has helped you understand the applications and benefits of each method, enabling you to make an informed decision about your health.
If you’re looking for precise and professional services in oral and jaw imaging, we recommend consulting Dr. Boushehri’s expertise. Dr. Boushehri, a specialist in oral, jaw, and facial radiology, offers the best services in this field, utilizing advanced equipment and reliable experience. You can schedule a consultation at his specialized center and benefit from practical guidance for your needs.
Additionally, if you have any questions regarding radiography or need more information, feel free to write your questions in the comments section. Dr. Boushehri will carefully answer your questions and address your concerns.